Understanding the Importance of Vital Signs
Crucial insights into vital signs: Discover the importance of monitoring heart rate, body temperature, and more for optimal health.

Understanding Vital Signs
The measurement and assessment of vital signs play a crucial role in healthcare. These objective measurements provide valuable information about the essential physiological functions of a living organism. Vital signs are the critical first step for any clinical evaluation, allowing medical professionals to assess wellbeing, diagnose health issues, and suggest necessary lifestyle changes.
Importance of Vital Signs
Vital signs are termed "vital" because of their significance in evaluating an individual's overall health status. These measurements provide critical information about the body's basic functions, allowing medical professionals to assess the functioning of various organ systems. By monitoring vital signs, healthcare providers can identify abnormalities or deviations from the baseline, which may indicate underlying health conditions or potential emergencies.
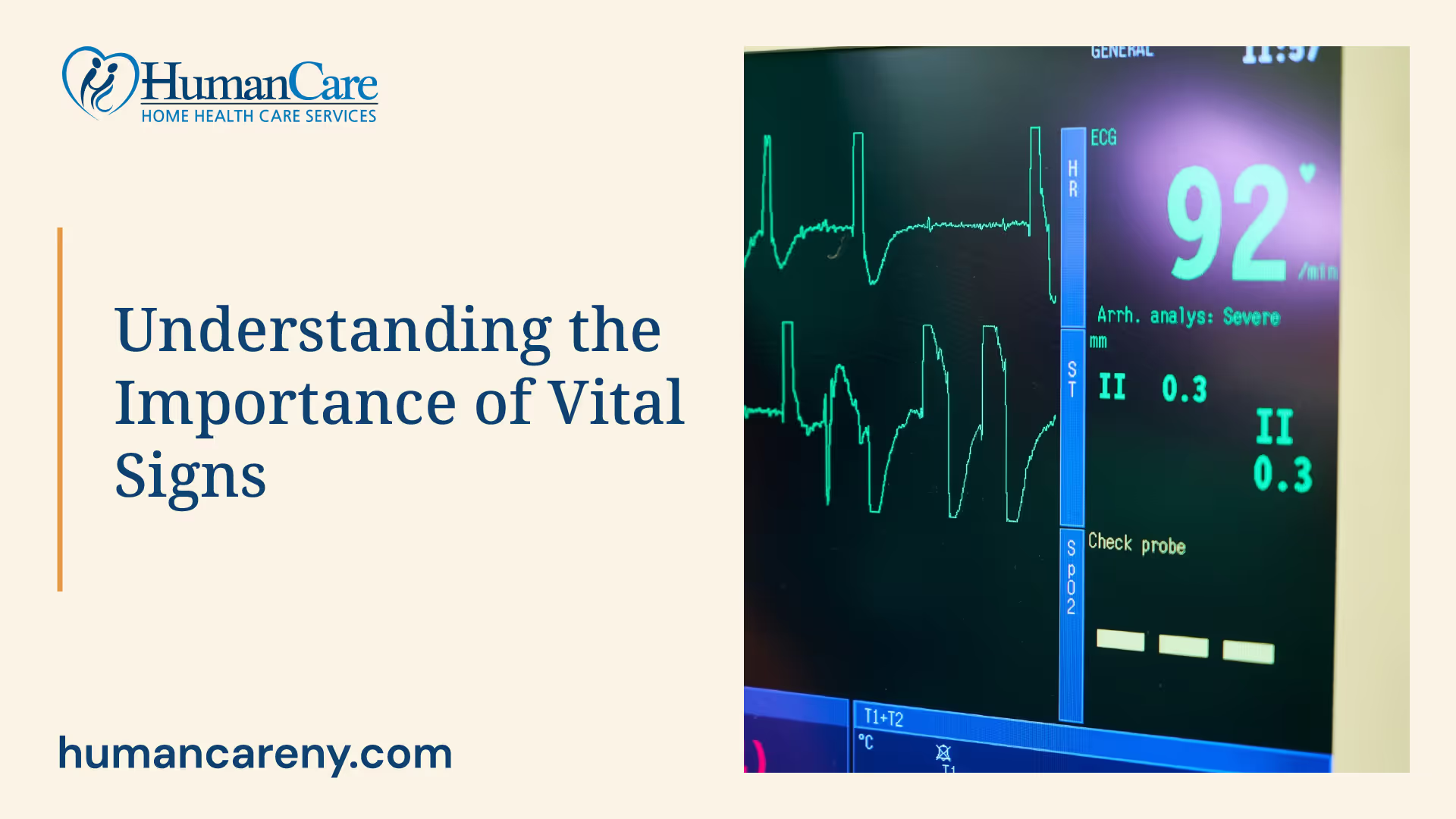
Vital signs serve as valuable indicators of a patient's physiological state, helping healthcare professionals in various ways. They aid in triaging patients in urgent care or emergency departments, allowing physicians to assess the degree of derangement from the baseline and prioritize patients accordingly. Vital signs also assist in monitoring patients during surgeries, identifying any adverse changes in health status, and guiding treatment decisions.
Role in Healthcare
Vital signs are an integral part of healthcare assessments, providing valuable insights into an individual's overall health and physiological functioning. They serve as the foundation for clinical evaluations, guiding medical professionals in diagnosing and managing various conditions.
By measuring and monitoring vital signs, healthcare providers can:
- Detect early signs of health deterioration or improvement.
- Assess the effectiveness of treatments and interventions.
- Evaluate the response to medications.
- Identify potential health risks or complications.
- Determine the need for further diagnostic tests or procedures.
The most common vital signs measured include heart rate, respiratory rate, body temperature, and oxygen saturation. These measurements, along with other assessments like blood pressure, height, and weight, help healthcare professionals gain a comprehensive understanding of a patient's health status. The data collected from vital signs can be used to establish a baseline for an individual's health and track changes over time, providing valuable information for ongoing management and treatment.
Understanding the importance of vital signs allows healthcare professionals to make informed decisions, provide appropriate care, and monitor the progress of patients effectively. By regularly assessing vital signs, healthcare providers can ensure the well-being of individuals and take necessary actions to promote health and prevent potential complications.
Key Vital Signs
Vital signs are essential indicators of a person's overall health and well-being. They provide valuable information about various bodily functions. The key vital signs include heart rate, respiratory rate, body temperature, and oxygen saturation.
Heart Rate
The heart rate refers to the number of times the heart beats per minute. It is a crucial vital sign that provides insights into cardiovascular health. The normal pulse rate for healthy adults ranges from 60 to 100 beats per minute University of Rochester Medical Center. However, it's important to note that heart rate can fluctuate due to factors such as exercise, illness, injury, and emotions. Athletes with high cardiovascular conditioning may have heart rates near 40 beats per minute.
Respiratory Rate
Respiratory rate refers to the number of breaths a person takes per minute. It is an indicator of lung function and overall respiratory health. The normal respiration rates for an adult person at rest range from 12 to 20 breaths per minute UW Medicine Health Library. Changes in respiratory rate can occur due to various factors such as physical activity, stress, or underlying medical conditions.
Body Temperature
Body temperature is a measure of the body's internal heat. It helps assess the body's ability to regulate temperature and detect potential abnormalities. The normal body temperature for a healthy adult is approximately 98.6 degrees Fahrenheit/37.0 degrees Celsius, ranging from 36.5 to 37.5 degrees Celsius (97.7 to 99.5 degrees Fahrenheit) Physio-Pedia. However, it's important to consider that body temperature can vary based on factors such as the site of measurement, time of day, gender, recent activity, physical fitness, food and fluid consumption, and stage of the menstrual cycle in women.
Oxygen Saturation
Oxygen saturation measures the percentage of hemoglobin in the blood that is carrying oxygen. It is a critical indicator of respiratory and circulatory health. Normal oxygen saturation levels for most healthy adults range between 95% and 100% Healthline. Levels below 95% indicate insufficient oxygen in the body and may require medical attention. Oxygen saturation can be checked at home using a pulse oximeter.
Understanding and monitoring these key vital signs provide valuable information for healthcare professionals to assess a person's health status, detect abnormalities, and make informed decisions regarding treatment or intervention. By regularly measuring and tracking vital signs, healthcare providers can monitor changes in a patient's condition and ensure appropriate care.
Normal Ranges
Vital signs provide essential information about an individual's overall health. Understanding the normal ranges for different vital signs helps healthcare professionals assess a person's well-being. Let's explore the normal ranges for heart rate, respiratory rate, body temperature, and oxygen saturation levels.
Heart Rate and Gender
The standard heart rate for a healthy adult ranges from 60 to 100 beats per minute, with slight variations based on sex assigned at birth. People assigned female at birth typically have slightly higher heart rates than people assigned male at birth. It is important to note that individual factors, such as age, fitness level, and overall health, may also influence heart rate.
Respiratory Rate Variations
A normal respiratory rate for a healthy adult usually falls between 12 to 16 breaths per minute. However, this rate may vary under different medical conditions or circumstances [3]. Factors such as physical activity, anxiety, or illness can influence the respiratory rate.
Body Temperature Fluctuations
The normal body temperature for adults ranges from 97.8°F to 99°F (36.5°C to 37.2°C), but it can fluctuate based on various factors like sex, recent activity, food consumption, and time of day [3]. The site of measurement, such as oral, rectal, or axillary, can also affect the recorded body temperature. It's important to note that body temperature can vary throughout the day, with it typically being lowest in the morning and highest in the late afternoon or evening.
Oxygen Saturation Levels
Oxygen saturation levels between 95% and 100% are considered normal for most healthy adults. Levels below 95% indicate insufficient oxygen in the body, requiring medical attention. Oxygen saturation can be checked at home using a pulse oximeter [3]. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional if oxygen saturation levels consistently fall below the normal range.
Understanding the normal ranges for vital signs allows healthcare providers to evaluate an individual's health status. Deviations from these ranges can indicate underlying health conditions or the need for further medical assessment. Regular monitoring of vital signs is crucial for maintaining overall well-being and identifying any potential health concerns.
Significance in Health Assessment
Vital signs play a significant role in health assessment, providing valuable information about the body's basic functions. They are crucial for monitoring patient status, predicting health outcomes, and guiding medical interventions. Let's explore three key aspects of the significance of vital signs in health assessment.
Triage and Emergency Care
In urgent care or emergency departments, vital signs are the initial indicators used for triaging patients. They help healthcare professionals quickly assess the severity of a patient's condition and prioritize treatment accordingly. Abnormal vital signs can signal potential life-threatening situations and the need for immediate intervention.
During triage, vital sign measurements such as heart rate, respiratory rate, blood pressure, and body temperature are assessed to determine the level of derangement from the baseline. This information aids physicians in making prompt decisions and allocating appropriate resources to patients based on the urgency of their conditions.
Predicting Health Outcomes
Vital signs abnormalities can serve as crucial indicators of long-term health outcomes. Studies have shown that certain vital sign variations can predict the likelihood of adverse events, return emergency department visits, and frequency of hospital readmissions. For example, an increased respiratory rate (>35 breaths per minute) has been strongly associated with life-threatening adverse events. Early warning score (EWS) tools, which utilize vital sign abnormalities, are instrumental in predicting cardiac arrest and death within 48 hours of measurement.
By closely monitoring vital signs and detecting any deviations from the normal range, healthcare professionals can intervene early, potentially preventing or mitigating adverse health outcomes.
Monitoring Patient Status
Vital signs are routinely monitored to assess patient status and evaluate the effectiveness of medical interventions. They provide valuable insights into the body's response to treatment, allowing healthcare professionals to adjust therapeutic approaches as needed.
Regular monitoring of vital signs helps in tracking changes in heart rate, respiratory rate, body temperature, and oxygen saturation levels over time. This longitudinal data provides a comprehensive picture of a patient's health status, enabling medical professionals to make informed decisions regarding ongoing care and treatment plans.
By closely monitoring vital signs, healthcare providers can identify trends, detect early warning signs of deteriorating health, and intervene promptly to prevent further complications.
Vital signs are an integral part of health assessment, playing a vital role in triage and emergency care, predicting health outcomes, and monitoring patient status. By understanding the significance of these measurements, healthcare professionals can provide optimal care and make informed decisions to promote patient well-being.
Measuring Vital Signs
Accurately measuring vital signs is an essential clinical skill that healthcare providers must possess. It requires both accuracy and precision to provide reliable information about a patient's health status. Let's explore the equipment and techniques used for measuring vital signs, as well as the importance of accuracy and precision in these measurements, along with the concept of inter-observer variability.
Equipment and Techniques
Healthcare professionals, including Emergency Medical Technicians (EMTs), paramedics, medical assistants, dental assistants, nurses, and physicians, are equipped with the necessary tools to measure vital signs. The specific equipment used for measuring vital signs varies depending on the particular sign being assessed. Here are some commonly used tools:
- Stethoscope: Used to listen to the heart and lung sounds, enabling the measurement of heart rate and respiratory rate.
- Thermometer: Used to measure body temperature, either orally, rectally, in the ear, or on the forehead.
- Sphygmomanometer: Used to measure blood pressure by applying pressure to the arm and listening for specific sounds using a stethoscope.
- Pulse oximeter: Used to measure oxygen saturation levels in the blood by clipping it onto a finger or earlobe.
Each tool requires specific techniques for accurate measurements. Healthcare providers are trained to follow standardized procedures and guidelines to ensure consistency and reliability in their measurements.
Accuracy and Precision
Accurate measurement of vital signs is crucial for providing a reliable overview of a patient's health status. Healthcare professionals must strive for accuracy to obtain precise measurements. Accuracy refers to how close the measured value is to the true value, while precision refers to the consistency and reproducibility of repeated measurements.
To ensure accuracy and precision, healthcare providers should adhere to the following guidelines:
- Use calibrated and properly functioning equipment.
- Follow standardized measurement techniques.
- Take measurements in a controlled environment, minimizing external factors that could affect the results.
- Allow sufficient time for measurements, as rushing can lead to errors.
- Record measurements accurately, including the unit of measurement and any relevant details.
Maintaining accuracy and precision in vital sign measurements is essential for providing reliable data that guides clinical decision-making and treatment.
Inter-Observer Variability
It's important to note that there can be variability in vital sign measurements when different healthcare providers assess the same patient. This phenomenon is known as inter-observer variability. Factors such as experience, technique, and equipment calibration can contribute to variations among observers.
To minimize inter-observer variability, healthcare providers should receive proper training and practice in measuring vital signs. Clinicians should also be aware of this variability and re-check vital signs themselves if there is a significant or unexpected change in the measurements. This helps ensure accuracy and consistency in assessing a patient's health status.
By understanding the importance of accuracy, precision, and inter-observer variability in measuring vital signs, healthcare providers can obtain reliable data for effective health assessment and monitoring.
Expanded Vital Sign Parameters
While the traditional vital signs play a crucial role in assessing a patient's health, there are additional parameters that can provide valuable insights. In this section, we will explore three expanded vital sign parameters: pulse oximetry, smoking status impact, and respiratory rate assessment.
Pulse Oximetry
Pulse oximetry is a non-invasive method used to measure the oxygen saturation level in a patient's blood. It involves placing a small device called a pulse oximeter on a finger or earlobe, which uses light absorption to determine the amount of oxygen present in the blood.
Monitoring oxygen saturation is vital in various clinical settings, such as during surgery, in intensive care units, or for patients with respiratory conditions. It helps healthcare providers assess the adequacy of oxygen delivery to the body's tissues. Normal oxygen saturation levels typically range from 95% to 100%.
Smoking Status Impact
Considering a patient's smoking status as an expanded vital sign parameter has shown significance in patient outcomes. The inclusion of smoking status allows healthcare providers to offer counseling and interventions to help patients quit smoking, which can greatly improve their overall health.
It's important to note that while some health care systems in the United States previously used "pain as the fifth vital sign," this approach has been abandoned due to the unintended opioid crisis. However, smoking status assessment continues to be valuable in promoting smoking cessation and reducing associated health risks.
Respiratory Rate Assessment
Respiratory rate assessment is another expanded vital sign parameter that provides valuable information about a patient's respiratory function. While vital sign assessment currently relies heavily on electronic equipment, studies have found that outside of intensive care units, respiratory rate assessment through observation can lead to insufficient, subjective, and unreliable results [1].
However, recognizing the importance of respiratory rate in identifying potential health risks, some early warning criteria and scoring systems incorporate abnormal respiratory rates. For example, a respiratory rate over 35 breaths per minute has been associated with life-threatening adverse events, and early warning score tools utilize vital sign abnormalities to predict cardiac arrest and death within 48 hours of measurement [1].
Accurately measuring and interpreting vital signs, including these expanded parameters, requires clinical skill and practice. It's important for healthcare providers to be aware of inter-observer variability and always re-check vital signs themselves if there is a significant or unexpected change. By incorporating these expanded vital sign parameters, healthcare professionals can gain additional insights into their patients' overall health and make informed decisions regarding their care.




























































































